It is impossible to work digitally without having some sort of workflow. Most are a bit better than adequate, some are good and some are blindingly awful. I think that it is important to have a look at the way you do things every once in a while to make sure that yours is as good as it can be and achieves the four goals of being;
- Efficient in terms of both time and memory
- Repeatable so that the purely functional bits can be done almost on auto-pilot
- Non destructive so that you don’t lose valuable RAW files or save changes to Jpegs shot in camera
- Able to be short-cut for jobs where time is even more of an issue
I’ve written about my workflow before and I often teach workshops based on the “photographer’s twelve step plan” – a process with 12 distinct stages from camera to client including backing up and having a coffee! In this blog post I’m simply going to go through my basic workflow with a few hints and tips as I go. I normally use Photo Mechanic to import, sort, caption, rename and export my files and Adobe Photoshop CC to convert RAW (Canon CR2 most of the time) files into the required format. The whole process is colour-managed and I do as much as I can in-camera to save myself time when editing. I work on either a MacBook Pro, a MacBook Air or a Mac Mini depending on where I am and what the job is. Anyway, let’s kick off…

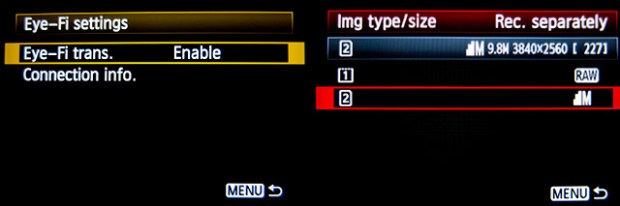
Before I insert a card into the card reader I launch Photo Mechanic. This screen grab shows the “general” preferences for the application including what I want to happen when I load a memory card. I have checked the box “Open as contact sheet(s)” which means that as soon as the card goes in I see the images in a standard window. In the past I often used “show ingest dialogue” but I have found that ingesting every single frame doesn’t suit me and that it slows the whole process down drastically. Typically I only want between 25% and 35% of the images and so I go through them using the “tag” function (cmd T on a Mac or ctrl T on a PC) to identify those that I’m interested in or those which have unique content.
Once I’ve been through that card and tagged the images I want I use the “copy” function (cmd Y on the Mac and ctrl Y on a PC) and copy those tagged files to a new folder. I use a simple formula YYMMDD-jobname-RAW for those files and then repeat this process with every card used on that job. Photo Mechanic can be set to automatically open and update a new contact sheet with the copied files. I always eject the cards without deleting anything just in case there are problems during the process and put those cards to one side to be deleted later.


The preview and contact sheet windows are extremely easy ways to look at and select pictures. Once I have my first edit done I apply a generic caption using the Photo mechanic stationery pad (cmd I or ctrl I). At this point I’d like to mention two enormously useful features of Photo Mechanic (available on some other applications too).
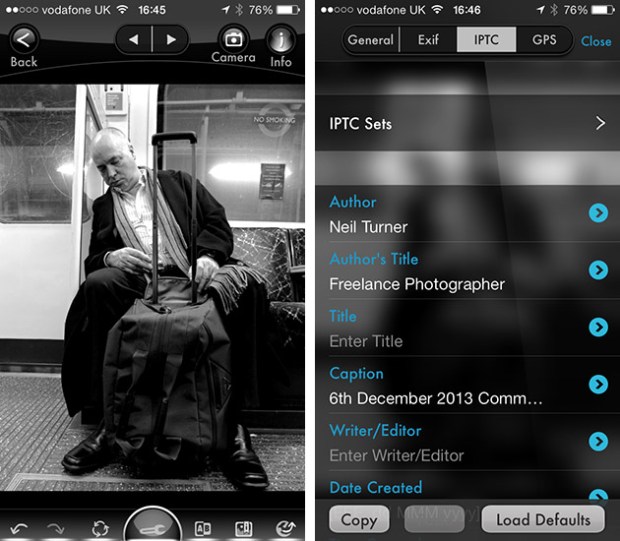
The first is variables. These are simple ways of automatically adding information to your captions or filenames. Many are derived from the EXIF data applied in the camera. These include time, day and date as well as other shooting data. Some cameras allow you to set copyright information in the camera and others apply GPS location data too. Other variables might include camera serial numbers, original filenames as well as items that you can add yourself from pre-loaded drop-down menus. I have every county in the United Kingdom loaded as well as a large number of towns and cities and I also have some specific locations where I work regularly pre-loaded. By choosing a specific city from one drop-down menu you can use variables to add it to relevant other areas of the IPTC automatically. You can see some examples of variables in the caption below.

My main caption starts with {city}, {state}. {iptcday0} {iptcmonthname} {iptcyear4} which will then become something like Brighton, East Sussex. 12 December 2013 if I have all of the right information ready to go. If there are more details to add to the generic caption it is easy enough to do those in batches using the stationery pad.
Variables can also be used in the renaming of files.

This requires you to add the IPTC caption before you rename the files because using the {headline} variable automatically includes the headline you have used in the filename. I find this to be very useful and very good for saving time. In practice Photo Mechanic will sequentially rename 100 files in about ten seconds using this method.
The other really useful feature that Photo Mechanic has for helping with captions is code replacement. The idea is similar to variables except you create your won shortcuts. Sports photographers use this a lot and it saves a great deal of time. Imagine a football (that’s soccer to everyone in north America) team with 22 squad players – many of whom have unfamiliar and difficult to spell names. Using code replacement you can preload a text file with the teams before the game using shirt numbers. The England team, for example, would have numbers from EN01 to EN22 with the names of the players set against those numbers. Using code replacement you would type \EN08\ and the software would immediately recognise that as 8 Wayne Rooney or whatever you have set it to say. I use it for political figures so \dcam\ automatically becomes The Rt Hon David Cameron MP. I can add a second part to that if I so wish \pm\ would add Prime Minister.
I also use code replacement for shooting musicians and bands. It is really easy to create a text file with the names of all of the band members and then use the shortcuts to add the relevant people to each frame. You select the shortcuts yourself and the long versions yourself. Once you get the hang of code replacement, it becomes a central part of your workflow.
At this point I’ll often do a second tighter edit. I’ll keep all of the RAW files that I have copied over from the cards but only convert and send the best to the client. For some news jobs that is only 6-10 images and for other editorial assignments anything between a dozen and thirty. Some of the corporate jobs I shoot end up with a couple of hundred files and working on those proves the efficiency of this workflow because it is scaleable and repeatable.
Once I have my RAW (CR2 or RAF) images selected, captioned and renamed it is time to highlight them all and open them in Adobe Camera RAW in Adobe Photoshop. There are a number of great RAW conversion options out there and whether you use Photoshop, Lightroom, Aperture, Capture One or any of the others you need to make sure that the one you use doesn’t strip your carefully added caption information during the RAW conversion process.

This is what the Adobe camera RAW window looks like. You can select a number of images from the strip down the left hand side and apply the same adjustments to all of them. I don’t want to run a complete ACR tutorial here but I would like to mention the straighten, sharpen, crop and lens correction adjustments as well worth learning. Of course those are secondary to the basic correction options such as colour temperature and tint, exposure, contrast, highlight and shadows etc. I find that I rarely need to open an image into Photoshop itself simply because all of the things that I’d normally do to a picture can be done right here in Camera Raw. Every few frames I will highlight those that have been corrected but not yet saved and save them. A decent computer with enough RAM will happily save the adjusted RAW files into whatever format you choose in the background whilst you continue to work on the rest. Once I have hit the “save” button on the last files I then click on “done”. Most of the time I am saving files at their default size as high quality Jpegs with some sharpening into the same folder as the RAW files. Photo Mechanic then updates the folder to show the RAW and Jpeg files together (you can separate them if you wish to) with a thumbnail from the newly saved Jpeg.
One of the best improvements between Adobe Camera RAW in Photoshop CS6 and Photoshop CC is an improved and expanded “save” dialogue window. You now have the option to set a target size, target amount of compression and apply a set degree of sharpening. With modern cameras producing pictures of over 60 megabytes and many of my clients wanting their photographs to be considerably smaller than that I am now using the target size more and more. My default setting is 4800 pixels along the longest side and with a maximum compressed file of 3200 kilobytes.

Once I have my images all saved I return to Photo Mechanic and copy the Jpeg files into a new folder ready to send to the client. More and more that folder is a Dropbox one and I will give the link to the images to the client. For news jobs I can simply FTP the images (having saved them at a smaller size) and for some commercial clients that means burning the pictures to a DVD or CD. However they are delivered, the images are correctly sized, nicely prepared from the RAW files and properly captioned and renamed. All of this is done quickly and efficiently without damaging any originals.
When the urgency of the edit is over, I copy the files to a RAID drive in my office, to a portable drive that lives in my car and to a third drive which is away from my office ‘just in case’. I might then treat myself to a coffee…
![]()